- coupled_varCoupled variable whose value is used in the criterion
C++ Type:std::vector<VariableName>
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:Coupled variable whose value is used in the criterion
- subdomain_idThe subdomain ID of the element when the criterion is met
C++ Type:unsigned short
Controllable:No
Description:The subdomain ID of the element when the criterion is met
- thresholdThe value above (or below) which to change the element subdomain
C++ Type:double
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:The value above (or below) which to change the element subdomain
CoupledVarThresholdElementSubdomainModifier
Modify the element subdomain ID if a coupled variable satisfies the criterion for the threshold (above, equal, or below)
Overview
The CoupledVarThresholdElementSubdomainModifier changes the element subdomain if a coupled variable meets a particular criterion. The threshold and criterion_type are used to determine this criterion. By default, the element changes subdomain if the averaged value of the coupled variable in the element is above the threshold. Other types of criterion are below and equal to the threshold value.
The CoupledVarThresholdElementSubdomainModifier inherits from the ElementSubdomainModifier. Details on solution reinitialization, stateful material property reinitialization and moving boundary/interface nodeset/sideset modification can be found in the description of the ElementSubdomainModifier.
Irreversible Modification
Consider a unit square domain, and an auxiliary variable defined by the function . The function represents a signed-distance function of a circle of radius whose center is moving along the x-axis towards the right.
Initially, the domain is decomposed by a vertical line . The elements on the left side of the vertical line have subdomain ID of 1, and the elements on the right side have subdomain ID of 2. The CoupledVarThresholdElementSubdomainModifier sets the coupled variable to be , and the criterion to be below a threshold value of 0, so all the elements within the moving circle will change subdomain ID from 2 to 1:
[moving_circle]
type = CoupledVarThresholdElementSubdomainModifier
coupled_var = 'phi'
criterion_type = 'BELOW'
threshold = 0
subdomain_id = 1
execute_on = 'INITIAL TIMESTEP_BEGIN'
[]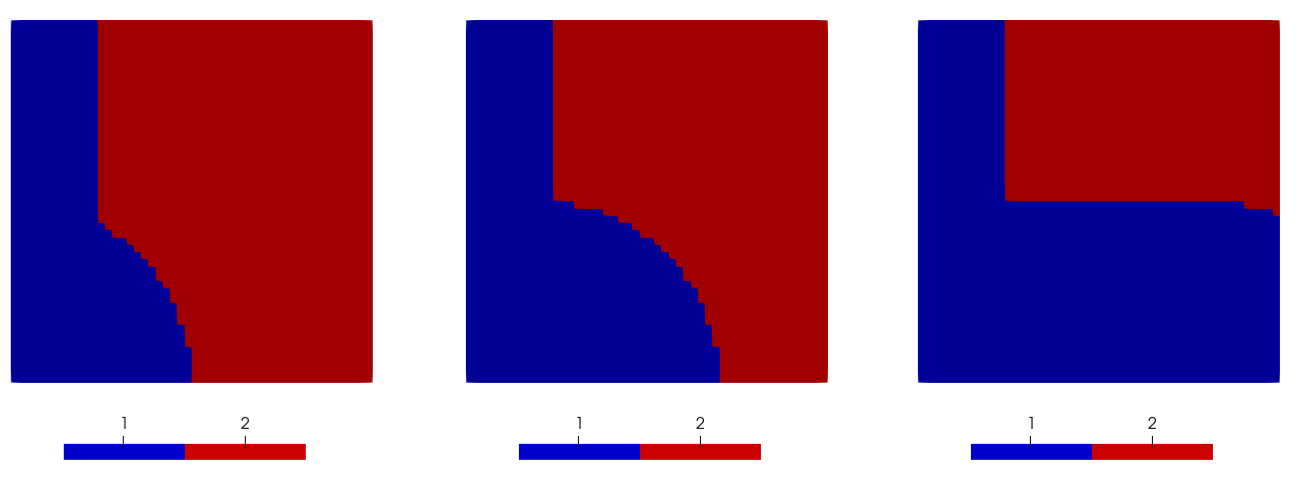
The result of a reversible element subdomain modifier at three different time steps
Reversible Modification
The irreversible modification is useful for applications suhc as element death and activation, but the subdomain modificationan can be changed to reversible by setting the parameter complement_subdomain_id to 2. Then the subdomain ID of all elements outside the circle will be set to 2:
[moving_circle]
type = CoupledVarThresholdElementSubdomainModifier
coupled_var = 'phi'
criterion_type = 'BELOW'
threshold = 0
subdomain_id = 1
complement_subdomain_id = 2
execute_on = 'INITIAL TIMESTEP_BEGIN'
[]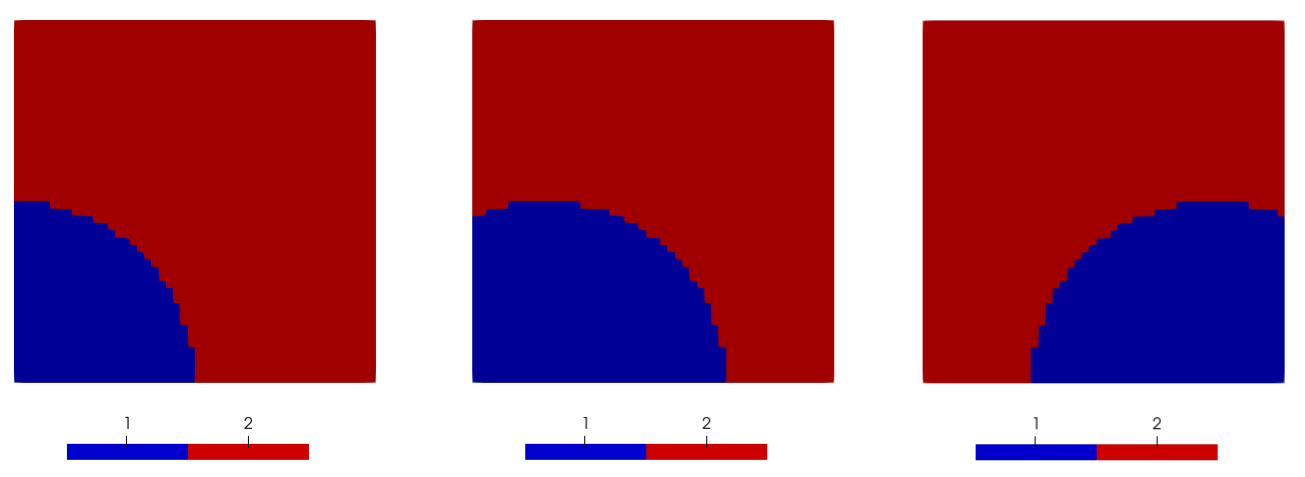
The result of a reversible element subdomain modifier at three different time steps
Input Parameters
- blockThe list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied
C++ Type:std::vector<SubdomainName>
Controllable:No
Description:The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied
- complement_subdomain_idThe subdomain ID of the element when the criterion is not met. If not provided, the element subdomain ID will not be modified if the criterion is not met.
C++ Type:unsigned short
Controllable:No
Description:The subdomain ID of the element when the criterion is not met. If not provided, the element subdomain ID will not be modified if the criterion is not met.
- criterion_typeABOVECriterion to use for the threshold
Default:ABOVE
C++ Type:MooseEnum
Controllable:No
Description:Criterion to use for the threshold
- moving_boundariesMoving boundaries between subdomains. These boundaries (both sidesets and nodesets) will be updated for elements that change subdomain. The subdomains that each moving boundary lies between shall be specified using the parameter 'moving_boundary_subdomain_pairs'. If one boundary and multiple subdomain pairs are specified, then it is assumed that the pairs all apply to the boundary. A boundary will be created on the mesh if it does not already exist.
C++ Type:std::vector<BoundaryName>
Controllable:No
Description:Moving boundaries between subdomains. These boundaries (both sidesets and nodesets) will be updated for elements that change subdomain. The subdomains that each moving boundary lies between shall be specified using the parameter 'moving_boundary_subdomain_pairs'. If one boundary and multiple subdomain pairs are specified, then it is assumed that the pairs all apply to the boundary. A boundary will be created on the mesh if it does not already exist.
- moving_boundary_subdomain_pairsThe subdomain pairs associated with each moving boundary. For each pair of subdomains, only the element side from the first subdomain will be added to the moving boundary, i.e., the side normal is pointing from the first subdomain to the second subdomain. The pairs shall be delimited by ';'. If a pair only has one subdomain, the moving boundary is associated with the subdomain's external boundary, i.e., when the elements have no neighboring elements.
C++ Type:std::vector<std::vector<SubdomainName>>
Controllable:No
Description:The subdomain pairs associated with each moving boundary. For each pair of subdomains, only the element side from the first subdomain will be added to the moving boundary, i.e., the side normal is pointing from the first subdomain to the second subdomain. The pairs shall be delimited by ';'. If a pair only has one subdomain, the moving boundary is associated with the subdomain's external boundary, i.e., when the elements have no neighboring elements.
- nearby_distance_threshold-1Threshold for considering elements as 'nearby' in the K-D tree search. Only elements within this distance will be considered for polynomial fitting.
Default:-1
C++ Type:double
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:Threshold for considering elements as 'nearby' in the K-D tree search. Only elements within this distance will be considered for polynomial fitting.
- nearby_kd_tree_leaf_max_size10Maximum number of elements in a leaf node of the K-D tree used to search for nearby elements. Only needed if 'reinitialization_strategy' is set to POLYNOMIAL_NEARBY.
Default:10
C++ Type:int
Controllable:No
Description:Maximum number of elements in a leaf node of the K-D tree used to search for nearby elements. Only needed if 'reinitialization_strategy' is set to POLYNOMIAL_NEARBY.
- old_subdomain_reinitializedTrueThis parameter must be set with a non-empty list in 'reinitialize_subdomains'. When set to the default true, the element's old subdomain is not considered when determining if an element should be reinitialized. If set to false, only elements whose old subdomain was not in 'reinitialize_subdomains' are reinitialized.
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:This parameter must be set with a non-empty list in 'reinitialize_subdomains'. When set to the default true, the element's old subdomain is not considered when determining if an element should be reinitialized. If set to false, only elements whose old subdomain was not in 'reinitialize_subdomains' are reinitialized.
- polynomial_fittersList of NodalPatchRecovery UserObjects used for polynomial fitting during variable reinitialization. Required only if 'reinitialization_strategy' includes POLYNOMIAL_NEIGHBOR, POLYNOMIAL_WHOLE, or POLYNOMIAL_NEARBY.
C++ Type:std::vector<UserObjectName>
Controllable:No
Description:List of NodalPatchRecovery UserObjects used for polynomial fitting during variable reinitialization. Required only if 'reinitialization_strategy' includes POLYNOMIAL_NEIGHBOR, POLYNOMIAL_WHOLE, or POLYNOMIAL_NEARBY.
- reinitialization_strategyIC The strategy used to reinitialize the solution when elements change subdomain. If multiple strategies are provided, each strategy will be applied to the corresponding variable. If only one strategy is provided, it will be applied to all variables.
Default:IC
C++ Type:std::vector<MooseEnum>
Controllable:No
Description:The strategy used to reinitialize the solution when elements change subdomain. If multiple strategies are provided, each strategy will be applied to the corresponding variable. If only one strategy is provided, it will be applied to all variables.
- reinitialize_subdomainsANY_BLOCK_ID By default, any element which changes subdomain is reinitialized. If a list of subdomains (IDs or names) is provided, then only elements whose new subdomain is in the list will be reinitialized. If an empty list is set, then no elements will be reinitialized.
Default:ANY_BLOCK_ID
C++ Type:std::vector<SubdomainName>
Controllable:No
Description:By default, any element which changes subdomain is reinitialized. If a list of subdomains (IDs or names) is provided, then only elements whose new subdomain is in the list will be reinitialized. If an empty list is set, then no elements will be reinitialized.
- reinitialize_variablesWhich variables to reinitialize when subdomain changes.
C++ Type:std::vector<VariableName>
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:Which variables to reinitialize when subdomain changes.
- restore_overridden_dofsA list of boolean flags, one for each variable in 'reinitialize_variables', specifying whether overridden DOF values should be restored after reinitialization for each variable. This is useful when the solved values on these DOFs should be preserved. If the list is empty, overridden DOF values will NOT be restored for any variable by default.
C++ Type:std::vector<bool>
Controllable:No
Description:A list of boolean flags, one for each variable in 'reinitialize_variables', specifying whether overridden DOF values should be restored after reinitialization for each variable. This is useful when the solved values on these DOFs should be preserved. If the list is empty, overridden DOF values will NOT be restored for any variable by default.
- skip_restore_subdomain_changesFalseSkip restoring the subdomain changes if the timestep is not advanced.
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Skip restoring the subdomain changes if the timestep is not advanced.
Optional Parameters
- allow_duplicate_execution_on_initialFalseIn the case where this UserObject is depended upon by an initial condition, allow it to be executed twice during the initial setup (once before the IC and again after mesh adaptivity (if applicable).
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:In the case where this UserObject is depended upon by an initial condition, allow it to be executed twice during the initial setup (once before the IC and again after mesh adaptivity (if applicable).
- execute_onTIMESTEP_ENDThe list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html.
Default:TIMESTEP_END
C++ Type:ExecFlagEnum
Controllable:No
Description:The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html.
- execution_order_group0Execution order groups are executed in increasing order (e.g., the lowest number is executed first). Note that negative group numbers may be used to execute groups before the default (0) group. Please refer to the user object documentation for ordering of user object execution within a group.
Default:0
C++ Type:int
Controllable:No
Description:Execution order groups are executed in increasing order (e.g., the lowest number is executed first). Note that negative group numbers may be used to execute groups before the default (0) group. Please refer to the user object documentation for ordering of user object execution within a group.
- force_postauxFalseForces the UserObject to be executed in POSTAUX
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Forces the UserObject to be executed in POSTAUX
- force_preauxFalseForces the UserObject to be executed in PREAUX
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Forces the UserObject to be executed in PREAUX
- force_preicFalseForces the UserObject to be executed in PREIC during initial setup
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Forces the UserObject to be executed in PREIC during initial setup
Execution Scheduling Parameters
- control_tagsAdds user-defined labels for accessing object parameters via control logic.
C++ Type:std::vector<std::string>
Controllable:No
Description:Adds user-defined labels for accessing object parameters via control logic.
- enableTrueSet the enabled status of the MooseObject.
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:Yes
Description:Set the enabled status of the MooseObject.
- implicitTrueDetermines whether this object is calculated using an implicit or explicit form
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Determines whether this object is calculated using an implicit or explicit form
- seed0The seed for the master random number generator
Default:0
C++ Type:unsigned int
Controllable:No
Description:The seed for the master random number generator
Advanced Parameters
- prop_getter_suffixAn optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any attempt to retrieve/get material properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
C++ Type:MaterialPropertyName
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:An optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any attempt to retrieve/get material properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
- use_interpolated_stateFalseFor the old and older state use projected material properties interpolated at the quadrature points. To set up projection use the ProjectedStatefulMaterialStorageAction.
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:For the old and older state use projected material properties interpolated at the quadrature points. To set up projection use the ProjectedStatefulMaterialStorageAction.