- cycle_frequencyThe frequency of the process. Used to calculate the period over which you are integrating.
C++ Type:double
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:The frequency of the process. Used to calculate the period over which you are integrating.
- cycles_between_modification0The number of cycles between the modifications of the postprocessor value
Default:0
C++ Type:double
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:The number of cycles between the modifications of the postprocessor value
- initial_valueThe initial value for this postprocessor
C++ Type:double
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:The initial value for this postprocessor
- reference_valueThe value that you want to the 'value' parameter to maintain
C++ Type:double
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:The value that you want to the 'value' parameter to maintain
- start_cycle1The number of cycles you want to wait before postprocessor value begins to be modified
Default:1
C++ Type:double
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:The number of cycles you want to wait before postprocessor value begins to be modified
- valueThe name of the postprocessor which will be compared to the reference
C++ Type:PostprocessorName
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:The name of the postprocessor which will be compared to the reference
PeriodicAmplitudeRegulator
PeriodicAmplitudeRegulator periodical updates its value based on the ratio of a coupled Postprocessor value and a reference value. The value of PeriodicAmplitudeRegulator is updated with the following scheme
Where is the new value of the PeriodicAmplitudeRegulator Postprocessor, is the reference value, is the value of the coupled Postprocessor, is the pervious value of the PeriodicAmplitudeRegulator Postprocessor, and the subscript is some multiplicative integer of the period.
Example Amplitude Regulation
PeriodicAmplitudeRegulator is intended to be used to modify the value of a control parameter to force another Postprocessor value to be equal a refernce value. For the test example periodic_modifier.i, the reference value was and the coupled Postprocessor was MultiPeriodAverager, which takes multiple period averages of a periodic integral that depends on the value of PeriodicAmplitudeRegulator. The results in the figure below are from the test example periodic_modifier.i with a more refined time step of dt = 1e-2. In this case, the Function Magnitude is the value of PeriodicAmplitudeRegulator with an initial value of and the Periodic Integral is the value of the coupled Postprocessor, MultiPeriodAverager.
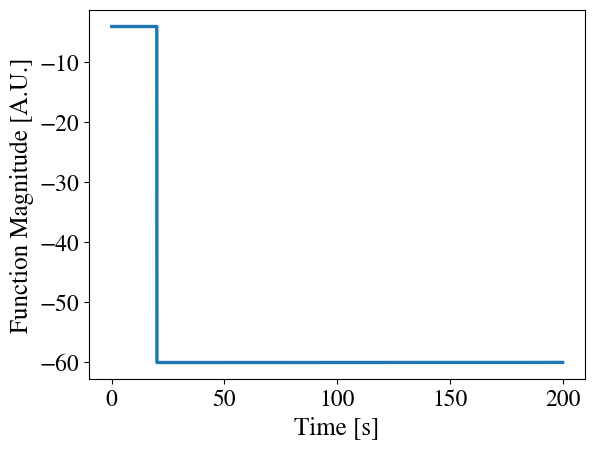
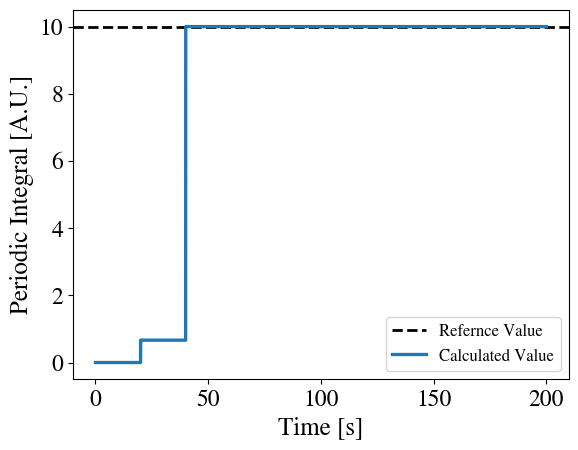
Example Input File Syntax
[Functions<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Functions/index.html"}>>>]
[func]
type = ParsedFunction<<<{"description": "Function created by parsing a string", "href": "../functions/MooseParsedFunction.html"}>>>
symbol_names<<<{"description": "Symbols (excluding t,x,y,z) that are bound to the values provided by the corresponding items in the vals vector."}>>> = 'mag'
symbol_values<<<{"description": "Constant numeric values, postprocessor names, function names, and scalar variables corresponding to the symbols in symbol_names."}>>> = 'mag'
expression<<<{"description": "The user defined function."}>>> = 'mag * x * (x-1)'
[]
[]
[Postprocessors<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Postprocessors/index.html"}>>>]
[a]
type = ElementIntegralVariablePostprocessor<<<{"description": "Computes a volume integral of the specified variable", "href": "ElementIntegralVariablePostprocessor.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object operates on"}>>> = v
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = 'initial timestep_end'
[]
[periodic_a]
type = PeriodicTimeIntegratedPostprocessor<<<{"description": "Integrate a Postprocessor value over a period in time using trapezoidal rule.", "href": "PeriodicTimeIntegratedPostprocessor.html"}>>>
value<<<{"description": "The name of the postprocessor you are integrating over time"}>>> = a
cycle_frequency<<<{"description": "The frequency of the process. Used to calculate the period over which you are integrating."}>>> = 0.1
coefficient<<<{"description": "The value to multiply the postprocessor by when integrating"}>>> = 0.1
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = 'initial timestep_end'
[]
[multi_period]
type = MultiPeriodAverager<<<{"description": "Calculate the average value of a post processor over multiple periods", "href": "MultiPeriodAverager.html"}>>>
value<<<{"description": "The name of the postprocessor you would like to average over multiple periods"}>>> = periodic_a
cycle_frequency<<<{"description": "The frequency of the process. Used to calculate the period over which you are integrating."}>>> = 0.1
number_of_periods<<<{"description": "The number of periods over which you are averaging"}>>> = 2
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = 'initial timestep_begin'
[]
[mag]
type = PeriodicAmplitudeRegulator<<<{"description": "Postprocessor that will modify its value by the ratio of anotherpostprocessor to the provided reference value", "href": "PeriodicAmplitudeRegulator.html"}>>>
value<<<{"description": "The name of the postprocessor which will be compared to the reference"}>>> = multi_period
cycle_frequency<<<{"description": "The frequency of the process. Used to calculate the period over which you are integrating."}>>> = 0.1
initial_value<<<{"description": "The initial value for this postprocessor"}>>> = -4
reference_value<<<{"description": "The value that you want to the 'value' parameter to maintain"}>>> = 10
start_cycle<<<{"description": "The number of cycles you want to wait before postprocessor value begins to be modified"}>>> = 2
cycles_between_modification<<<{"description": "The number of cycles between the modifications of the postprocessor value"}>>> = 2
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = 'initial timestep_end'
[]
[]Input Parameters
- allow_duplicate_execution_on_initialFalseIn the case where this UserObject is depended upon by an initial condition, allow it to be executed twice during the initial setup (once before the IC and again after mesh adaptivity (if applicable).
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:In the case where this UserObject is depended upon by an initial condition, allow it to be executed twice during the initial setup (once before the IC and again after mesh adaptivity (if applicable).
- execute_onTIMESTEP_ENDThe list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html.
Default:TIMESTEP_END
C++ Type:ExecFlagEnum
Controllable:No
Description:The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html.
- execution_order_group0Execution order groups are executed in increasing order (e.g., the lowest number is executed first). Note that negative group numbers may be used to execute groups before the default (0) group. Please refer to the user object documentation for ordering of user object execution within a group.
Default:0
C++ Type:int
Controllable:No
Description:Execution order groups are executed in increasing order (e.g., the lowest number is executed first). Note that negative group numbers may be used to execute groups before the default (0) group. Please refer to the user object documentation for ordering of user object execution within a group.
- force_postauxFalseForces the UserObject to be executed in POSTAUX
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Forces the UserObject to be executed in POSTAUX
- force_preauxFalseForces the UserObject to be executed in PREAUX
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Forces the UserObject to be executed in PREAUX
- force_preicFalseForces the UserObject to be executed in PREIC during initial setup
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Forces the UserObject to be executed in PREIC during initial setup
Execution Scheduling Parameters
- control_tagsAdds user-defined labels for accessing object parameters via control logic.
C++ Type:std::vector<std::string>
Controllable:No
Description:Adds user-defined labels for accessing object parameters via control logic.
- enableTrueSet the enabled status of the MooseObject.
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:Yes
Description:Set the enabled status of the MooseObject.
- outputsVector of output names where you would like to restrict the output of variables(s) associated with this object
C++ Type:std::vector<OutputName>
Controllable:No
Description:Vector of output names where you would like to restrict the output of variables(s) associated with this object
- use_displaced_meshFalseWhether or not this object should use the displaced mesh for computation. Note that in the case this is true but no displacements are provided in the Mesh block the undisplaced mesh will still be used.
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Whether or not this object should use the displaced mesh for computation. Note that in the case this is true but no displacements are provided in the Mesh block the undisplaced mesh will still be used.
Advanced Parameters
- prop_getter_suffixAn optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any attempt to retrieve/get material properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
C++ Type:MaterialPropertyName
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:An optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any attempt to retrieve/get material properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
- use_interpolated_stateFalseFor the old and older state use projected material properties interpolated at the quadrature points. To set up projection use the ProjectedStatefulMaterialStorageAction.
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:For the old and older state use projected material properties interpolated at the quadrature points. To set up projection use the ProjectedStatefulMaterialStorageAction.